Moving from Manual Systems – Automation in Progress for Tissue Bank Establishments
The tissue (human cells, tissues, and cellular and tissue-based products – HCT/Ps) banking industry is highly regulated and faces unique challenges in regulatory compliance, data integrity, and operational efficiency while ensuring patient and product safety, quality, and traceability is maintained. As establishments seek to modernize and transition from manual processes to automation and implement Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, it’s crucial to understand the regulatory landscape and manage associated risks effectively as set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Let’s explore the essential considerations for tissue establishments embarking on this transformative journey!
The FDA regulates HCT/Ps under 21 CFR Part 1271 which outlines the requirements for Good Tissue Practices (GTP), documentation controls, tracking and traceability from donor to recipient (and vice versa). Compliance with these regulations is paramount for ensuring patient and product safety and quality. When transitioning to automated workflows and ERP, tissue establishments must ensure all electronic records, signatures [1] , and systems [2] meet FDA’s requirements and that system implementation and/or changes do not introduce compliance risks.
While manual processes may offer flexibility, they are prone to human error, inefficiency, and difficulty in scaling. Automation and ERP systems can streamline operations, enhance data accuracy, and improve compliance. However, this transition requires careful planning and consideration of the following:
Define Requirements - identify your organization’s business needs and regulatory requirements.
Gap Assessment/Process Mapping – perform a gap assessment and evaluate current manual processes against regulatory requirements and identify gaps that automation and ERP can address. Document all existing manual processes to identify inefficiencies and compliance gaps before automation.
System Selection – choose ERP and automation systems that are designed for the intended use of the industry (e.g., life sciences, medical device, etc.), integration, scalability and flexibility, user training, and supports regulatory requirements.
Develop a Validation Master Plan and Validate [3] – Outline a risk-based validation approach according to your organization’s needs and regulatory expectations including, but not limited to, Installation Qualification – IQ, Operational Qualification – OQ, Performance Qualification – PQ.
Data Migration – ensure that historical data is accurately transferred and validated in the new system, maintaining integrity and traceability.
Change Management and Training – provide comprehensive training to staff and manage organizational change and resources to foster adoption and minimize business disruption.
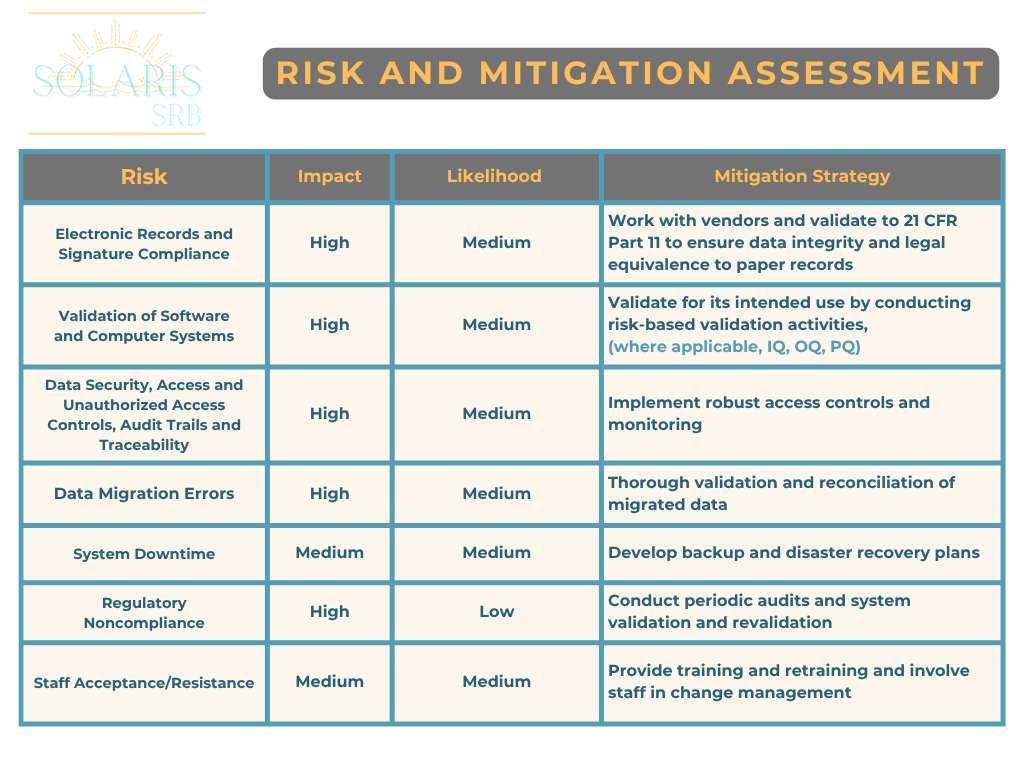
Risk and Mitigation Assessment
Transitioning introduces new risks including system failures, data breaches, and compliance gaps. Using quality tools such as a risk chart to systematically approach risks will help identify, assess, and mitigate these risks. Please see below for an example of a risk chart:
Consider best practices for a successful transition such as:
Involve cross-functional teams early in the process to identify needs and keep communication leveled with expectations for the overall picture.
After implementation, continuously improve by monitoring system performance and regulatory compliance, make improvements and revalidate as needed based on the risk.
Stay updated on FDA and other regulatory standards and requirements to ensure ongoing compliance.
Work closely with ERP vendors to ensure system customization aligns with FDA requirements and business needs.
For tissue establishments, the transition from manual processes to automation and ERP solutions offers significant opportunities for improving operational efficiency, reducing errors, data integrity, and regulatory compliance. It’s essential to address regulatory requirements at every stage of the transition and foster a culture of continuous improvement and compliance. By focusing on electronic records compliance, system validation, data security, and best practices, companies can confidently navigate the complexities of automation and achieve a seamless, compliant, and successful digital transformation.
If you haven’t checked out one of our previous blogs on software validation, check it out here!
Have questions? Contact us here!
References
[1] https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-11
[2] https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-L/part-1271